Study area
The study was conducted in Ekiti state, specifically ABUAD, Ado-Ekiti town, the capital of Ekiti state in southwestern Nigeria. ABUAD is a prominent educational institution in Ekiti with an average student population of 800,021. ABUAD is a private university in Nigeria known for its advanced e-learning platform and modern educational facilities such as electronic whiteboards. Our university is comprised of six faculties: Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy, Faculty of Law, Faculty of Engineering, Faculty of Science, and Faculty of Social and Management Sciences, and conducts a wide variety of undergraduate research.
Complementing these academic resources is the Afe Babalola University Multisystem Hospital (AMSH), which provides comprehensive medical services to the university community. AMSH is staffed by a diverse group of medical professionals, including physicians, nurses, and support staff, who are dedicated to providing quality health care. The hospital operates 24 hours a day, ensuring students have access to medical services at all times, whether for emergencies or routine medical needs.
research design
This study utilized a cross-sectional design and adopted a descriptive survey approach to collect information.
Study population and period
This study was conducted between April and May 2023 among undergraduate students at ABUAD.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The study included undergraduate students from selected universities who expressed a willingness to participate. Conversely, individuals who did not complete the questionnaire during the study period were excluded from the study.
Determining sample size
The sample size was determined using Taro Yamane’s (1973) formula 22.
$$\:n=\frac{N}{1+N\:\left({e}^{2}\right)}\:$$
where.
n = minimum sample size.
N = accessible population.
e = significance level = 0.05.
Sample size was determined using a formula based on a study population of 8,000 participants, a desired significance level of ± 5%, and a 10% adjustment for potential nonresponse. The calculated sample size was 423.
Sampling method
A multistage sampling technique was adopted to select participants for the study.
Stage 1:
A simple random sampling technique was used with computer-generated code to select four of ABUAD’s six universities. The decision not to include higher levels of sampling, such as departments, is based on the university’s organizational structure, which consists of colleges and departments.
Stage 2:
Two departments from each university were selected using a simple random sampling technique in computer-generated code. This method ensured that each faculty had an equal and fair chance of being selected. This approach was taken because each university in ABUAD typically contains at least two faculties, with the exception of the Faculty of Law, which has one faculty. Proportional allocation was then used to determine the number of students sampled from each department based on their relative size within the university (Table 1). Within each faculty, students were randomly selected to participate in the study. This was done by assigning a number to every student within the department and using a random number generator to select the desired number of participants. The link to the online survey was shared with selected students from each faculty.
To ensure the validity of responses, rigorous efforts were made to limit access to the survey to eligible individuals.
Access control:
The online survey was distributed via a Google Forms link that was accessible only to students in the selected departments. Access was restricted to ensure that only eligible participants could respond.
verification:
Participants were required to confirm their student status before proceeding with the survey to ensure that only current ABUAD students were included in the study.
Response limits:
The Google Form link was programmed to automatically stop accepting responses once a predetermined number of participants from each department was reached. This measure helped maintain sample integrity and data reliability.
Table 1 Proportional distribution of sample size based on university and department breakdown.
Equipment for data collection
A 21-item semi-structured questionnaire was designed to address the study objectives. The survey consists of four sections: socio-demographics, utilization of health care services, student perceptions, and economic factors influencing health care utilization. The survey included multiple choice, Likert scale, and dichotomous questions.
The first section assessed participants’ sociodemographics by collecting information on age, gender, marital status, and religion. Section B assessed ABUAD students’ health service utilization using three questions including yes/no and multiple-choice formats. Section C assessed students’ perceptions of health service utilization. This section consists of five questions measured using a 4-point Likert scale, with “Strongly Agree” being the highest ranked (assigned a score of 4) and “Strongly Disagree” being the lowest ranked (assigned a score of 1). was assigned). Student perceptions were quantified by summing student responses to five relevant questions. The possible total scores for each student range from 5 (if the student selects “strongly disagree” for all questions) to 20 (if the student selects “strongly agree” for all questions). ) range. To classify these perceptions as positive and negative, we compared each student’s total score to the midpoint of the possible score range, 12.5. Perceptions with a total score of 12.5 or higher (50% or more of the maximum possible score) were classified as positive, and recognitions with a total score of less than 12.5 (less than 50% of the maximum possible score) were classified as positive. Negative… The fourth section assessed the economic factors that influence the utilization of health services among ABUAD students. A total of three questions were measured on a four-point Likert scale. “Strongly agree” was ranked highest, and “strongly disagree” was ranked lowest.
Validity and reliability
Content validity was ensured by the academic staff of the Faculty of Public Health, Afe Babalola University. A pretest was also conducted with 20 participants who were not included in the main sample. As a result, the Cronbach alpha reliability coefficient was 0.720, indicating high reliability.
Data collection and analysis
The self-administered online survey was shared through selected departmental WhatsApp groups, and informed consent was obtained before participants accessed the survey. This ensured that only students from selected departments could access the Google Forms link and participate in the study. Descriptive statistics were used for categorical variables, and binary logistic regression analysis was used to assess the relationship between student perceptions and associated factors, and the relationship between student perceptions and health service utilization. In this study, logistic regression was used to determine the influence of various social, perceptual, and economic factors on the utilization of health services among students of Afe Babalola University. This statistical method models the relationship between a binary dependent variable (in this case, health service utilization) and one or more independent variables (such as gender, family size, age, perceptions of health services, and economic factors). Helpful.
Logistic regression analysis steps
Definition of dependent variable
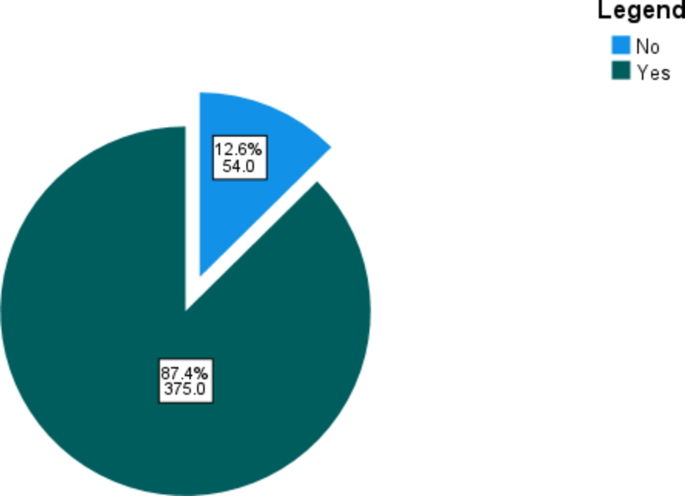
The dependent variable in this analysis is health service utilization, which is dichotomous (0 = not utilized, 1 = utilized).
Independent variables include:
social factors
Gender, family structure, age.
sensing
Attitude towards staff, distance to facility, waiting time, competency of medical staff.
economic barrier
Service costs, food costs, medicine costs, family income, monthly allowance.
Perceptions of medical services were defined by four main variables: attitude toward staff, distance to facility, waiting time, and competency of medical staff. Each variable was measured using a Likert scale. Health service utilization was defined as at least one visit to a health center in the past 6 months. Individual variables were included in a logistic regression analysis to identify significant predictors of health care utilization.
When analyzing students’ perceptions of health services, it was essential to focus on students who had first-hand experience with these services. Therefore, students who reported never using medical services at the academic medical center were excluded from the cognitive analysis. This exclusion ensures that the cognitive analysis accurately reflects the opinions of those with direct experience.
Perception factors considered students’ opinions regarding the attitude of medical staff, the distance of the facility from the hostel, waiting time, and the competency of the staff. Financial barriers included students’ opinions about the affordability of services and food, the impact of high drug costs, household incomes of different demographics, and monthly allowances. Also, prior to the logistic regression analysis, the variable responses to perceptions and economic barriers were dichotomized into agree or disagree.
In our study, “financial barriers to utilization of health services” was assessed using three Likert scale questions. These questions asked participants to indicate their level of agreement (from 1 = strongly disagree to 4 = strongly agree) with statements regarding the economic aspects of access to health services.
For the purpose of binary logistic regression analysis, responses were categorized into two groups.
“Agree” category: Includes participants who selected “Agree” or “Strongly Agree.”
“Disagree” category: This includes participants who selected “disagree” or “strongly disagree.”
This binary classification allowed us to create a dichotomous variable for each economic barrier question. In the regression model, we used “agree” as the reference category. This means that the odds ratio generated from the regression analysis represents the likelihood of facing economic barriers (defined by disagreement with the statement) compared to the reference group (the group who agreed with the statement). means.
Statistical Product and Service Solutions (IBM SPSS) version 27 facilitated data analysis with the significance level set at 5%.
This study received ethics approval from the Afe Babalola University Health Research Ethics Committee (ABUADHREC) prior to commencement, with approval number ABUADHREC/19/05/2023/91. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or legal guardians to ensure their voluntary participation. This study was conducted with strict guarantees of confidentiality of all information provided by participants. Furthermore, all methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations, including the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.