Cells and viruses
HEK293T and Vero E6 cells were obtained from ATCC. These adherent cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin (ThermoFisher) and 10% FBS (ThermoFisher). HEK293T expressing hACE2 (hACE2/HEK293T) was constructed. Expi293F suspension cells were stored in Union 293F (Union) containing 8 mM glutamine (ThermoFisher), and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (ThermoFisher) and placed on a polycarbonate vented conical flask shaker at 37 °C, 8% CO2, and a shaker at 120 rpm. All cells were regularly tested for mycoplasma DNA using PCR, and it confirmed that they were mycoplasma-free. The authentic SARS-CoV-2 virus, isolated and authorized by Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, was carried out in the BSL-3 facility at Sun Yat-sen University.
Animal models
The Bcl6fl/fl and CD4Cre mice were purchased from Jackson’s laboratory and genotypes were confirmed by PCR. Bcl6fl/fl mice were crossed with Cd4Cre mice to generate CD4creBcl6fl/fl mice. 6 to 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice of Specific Pathogen Free (SPF) were purchased from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center. The numbers of mice used for the C57BL/6 and CD4CreBcl6fl/fl strains were indicated in the figure legends. All mice were raised and vaccinated in the SPF facilities at the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University. For animal welfare ethics, mice were euthanized by isoflurane inhalation followed by cervical dislocation according to predefined endpoints, i.e., at the end of the experimentation (the last timepoint for analysis post vaccination indicated in the figures), or when animals exhibited signs of cachexia, prolonged behavioral abnormalities, or physical impairment.
Protein Expression and Purification
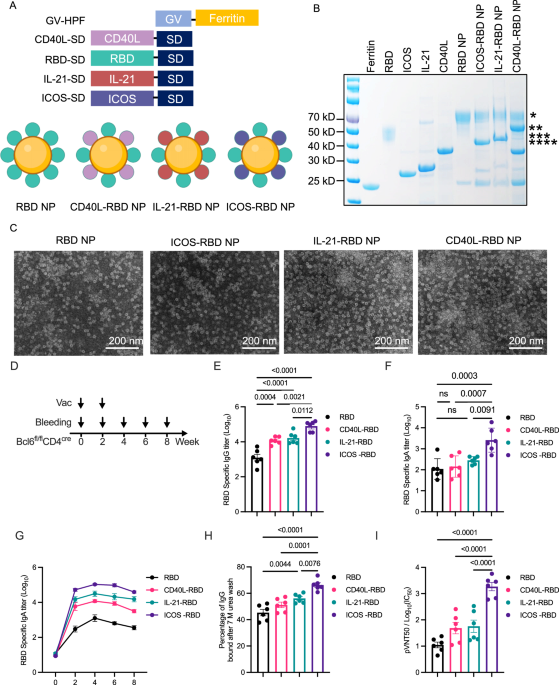
The construction of the RBD nanoparticle vaccine was described in the manuscript. To further improve the binding efficiency of the nanoparticle vaccine, the Gv/Sd system was used to enhance the efficiency of the SARS-CoV-2 nanoparticle vaccine. Gv-HPF could be self-assembled to be a 24-mer nanoparticle and conjugated with RBD-Sd robustly. Gv-HPF was expressed and purified from prokaryotic expression of BL21 bacteria (Vazyme) induced by Isopropylthio-β-galactoside (IPTG). The bacterial cultures were harvested and lysed by sonication in Tris buffer (20 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, pH 7.5). The lysate supernatants were heated to 65 °C for 15 min to precipitate most of the Escherichia coli proteins. Sequences of mCD40L, mIL-21, mICOS were obtained by overlap PCR, and then connected with Sd-tag, to be inserted into pET28a vector using NocI and XhoI sitess. Similarly, the constructs were transformed into Rosetta (Solarbio) for expression and purification. The sequences of Delta-RBD, Beta-RBD, JN.1-RBD, and HIV-MD39 were cloned into the pcDNA3.1 vector, followed by expression and purification from Expi293F cells. The RBD or HIV MD39 were genetically fused with Sd-Tag at the N-terminus, which could be conjugated with Gv-HPF in the manner of an isopeptide bond. Seven days after transfection, the supernatants were collected and the cellular debris were discarded by centrifugation. The supernatants were passed through Ni-NTA agarose four times to enrich His-tagged target proteins and then eluted with Tris buffer containing imidazole. After centrifugation and concentration, the supernatants were loaded onto a Superose 6 Increase (GE Healthcare) size-exclusion column and eluted with the Tris buffer at a rate of 0.5 mL min−1. The concentration of Gvo-protein was determined by the BCA assay method. The bacterial endotoxins in nanoparticles were quantified by the Tachypleus amebocyte lysate test (≤ 10 EU per dose). All purified proteins were confirmed by gel electrophoresis of SDS-PAGE with Coomassie blue staining.
Animal vaccination
The CD4creBcl6fl/fl mice were subcutaneously immunized at days 0 and 14 with two doses of Alum-adjuvanted RBD, CD40L-RBD, IL-21-RBD, or ICOS-RBD nanoparticles, in equimolar of 6 ug equivalent of RBD nanoparticle, respectively. Serum was collected at days 0, 14, 28, 42, and 64. A verified anti-ICOSL antibody, clone HK5.3 (BioLegend 107412), was used for in vivo blockade. 500 ug of HK5.3 antibody was intravenously injected into each mouse to block ICOSL. Twenty-four hours later, ICOS-RBD or RBD nanoparticles were used to immunized the HK5.3 antibody-treated mice to determine the influence of ICOS/ICOSL on the vaccine efficacy. For HIV-1 vaccination experiments, the CD4creBcl6fl/fl mice were subcutaneously immunized at days 0 and 14 with two doses of Alum-adjuvanted MD39 or ICOS-MD39 nanoparticles, in equimolar of 6 ug equivalent of MD39 nanoparticle, respectively.
SARS-CoV-2 infection
The CD4creBcl6fl/fl mice, immunized with indicated vaccines, were challenged with authentic SARS-CoV-2 Omicron EG.5 strain in the BSL-3 facility. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and inoculated intranasally with 5 × 104 FFU of SARS-CoV-2 viruses. The lungs were collected at day 5 post-infection (d.p.i.).
Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
The lungs of challenged CD4creBcl6fl/fl mice were collected and homogenized with gentleMACS M tubes (Miltenyi Biotec, 130-093-236) in a gentle-MACS dissociator (Miltenyi Biotec, 130-093-235). RNAs were extracted using RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN, 4104) according to the manufacturer’s instruction, followed by the qRT-PCR to determine the viral RNA copies of lung tissues utilizing a one-step SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing) (Da An Gene Co., DA0931). The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) gene was cloned into a pcDNA3.1 expression plasmid for standards to generate a standard curve. The indicated copies of N standards were ten-fold serially diluted from 109 to 102 and proceeded to qRT-PCR utilizing the same one-step SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection kit to obtain standard curves. The reactions were carried out on a BioRad CFX according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The viral RNA copies of each tissue were calculated into copies per µg total RNA and presented as a log10 scale.
Histopathology and immunohistochemistry
The CD4creBcl6fl/fl mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2 were euthanized in the BSL-3 facility. Lungs were collected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde buffer for 48 h at 4 ˚C, followed by embedding with paraffin. Longitudinal sections were performed on these tissues. The sections (3–4 µm) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). For immunohistochemistry, lung sections of each mouse were incubated with rabbit anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein (N) at 1:1000 dilution, and the IHC was conducted as published before.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The recombinant RBD-Sd and MD39-Sd proteins were diluted to 5 µg mL−1 with coating buffer and coated on high-binding 96-well plates (Corning) overnight at 4 °C, respectively. After washing with PBS three times, the plates were blocked with 5% non-fat milk/PBS for 1 h at room temperature. The plates were washed three times with PBST (containing 1% Tween-20) again, and the animal serum was diluted serially in PBS, followed by incubating the plates for 1 h at 37 °C. After washing with PBST, HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG, goat anti-mouse IgG1, and goat anti-mouse IgG2c were added at a dilution of 1:4000, 1:3000, and 1:3000 to detect antigen-specific each isotype antibody in serum of mice. After incubating for another 1 h, the plates were washed with PBS/T. Subsequently, 50 µL HRP substrate TMB solution (eBioscience) per well was added under dark, and the reaction was terminated with a stop solution (Solarbio) after sufficient development. The absorption was measured at 450 nm. GraphPad Prism 9.0 software was used to perform non-linear regression analysis on the data to calculate the endpoint titer.
7M Urea Avidity ELISA
Coat ELISA plates overnight at 4°C with 5 μg/ml antigen protein in 0.1 M bicarbonate buffer (pH 9.3). After washing with PBS three times, the plates were blocked with 5% non-fat milk/PBS for 1 h at room temperature. The plates were washed three times with PBST (containing 1% Tween-20) again, and the animal serum was diluted serially in PBS, followed by incubating the plates for 1 h at 37 °C. After incubation with diluted serum, wash plates twice with PBS/T. Incubate the wells with PBST or PBST/7M Urea for 10 minutes at room temperature. After washing with PBS/T, HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG was added at a dilution of 1:4000 to detect antigen-specific antibody in the serum of mice. After incubating for another 1 h, the plates were washed with PBST. Subsequently, 50 µL HRP substrate TMB solution (eBioscience) per well was added under dark, and the reaction was terminated with stop solution (Solarbio) after sufficient development. The absorption was measured at 450 nm. GraphPad Prism 9.0 software was used to perform non-linear regression analysis on the data to calculate the endpoint titer. Calculate the avidity index for each serum sample by dividing readings from 7 M Urea treatment by readings from PBST-only treatment.
Pseudotyped virus neutralization assay
The generation protocol was described as published before.(4) In brief, the plasmid expressing the respective mutant pseudotyped virus spike protein of Delta, was constructed. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with the psPAX2 (Addgene) plasmid, the lentiviral plasmid expressing luciferase (Addgene), and the plasmid expressing the respective mutant spike by using polyethyleneimine (PEI, Sigma). 48 h after transfection, the culture supernatant was collected and filtered with a 0.20 µm filter and then stored at −80 °C. Virus titration was performed by serially diluting the viral infection of hACE2-293T cells, and the infectivity was measured by detecting luminescence. The serum of all immunized animals was serially diluted and incubated with a pre-titrated amount of pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 virus at 37 °C for 1 h. Subsequently, the serum/virus mixture was added to the wells containing 2 × 104 hACE2-293T cells and incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 48 h. Then the cells were lysed with lysis buffer (Promega), and the lysate was measured by detecting the relative luminescence unit (RLU) in the photometer (Promega) to measure the luciferase activity. GraphPad Prism 9.0 software was used to analyze the serum-neutralizing antibody titers of the pseudotyped virus.
Cell isolation
The spleen or draining lymph nodes were collected and homogenized through a 70 µm strainer in PBS. The red blood cells (RBCs) were removed by adding ACK lysis buffer, followed by centrifuging to discard the supernatant and resuspended the cells with PBS. Mouse primary B cells were isolated by Mouse B Cell Separation Kit (RWD, K1305-20) according to the instruction.
Flow cytometry
Single-cell suspension was stained with fluorochrome-conjugated monoclonal antibodies for 20 min within PBS containing 0.5% BSA on ice. LIVE/DEAD Fixable Viability Dyes (Thermo) were used to gate live cells. The following indicated antibodies were used: CD3- FITC (17A2, Biolegend 100204) CD19-BV510 (6D5, Biolegend 115546), B220-APC/Fire™ 750 (RA3-6B2, Biolegend 103260), B220-APC (RA3-6B2, Biolegend 103212), CD38-PE (90, Biolegend 102707), CD38-PercP5.5(90, Biolegend 102721), IgD-PE(11-26c.2a, Biolegend 405705), IgD-APC (11-26 c.2a, Biolegend 405713), CD95-PE-Cy7 (SA367H8, Biolegend 152617), CD95-PE(SA367H8, Biolegend 152607), GL7-APC (GL7, Biolegend 144617), GL7-FITC (GL7, Biolegend 144604), CD138-BV421 (281-2, Biolegend 142507), CD138-PE(W20051E, Biolegend 142503) CD21-FITC(7E9, Biolegend 123407), CD23-PE(B3B4, Biolegend 101607), ICOSL-PE(HK5.3, Biolegend 107405), ICOSL-Biotin (HK5.3, Biolegend 107403) Streptavidin-BV421(Biolegend 405226), Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) (Biolegend, 423401), AnnexinV-PB(Biolegend, 640918), Brdu-AF488(Biolegend, 364106) The flow data were collected by BD LSRFortessa and analyzed with Flowjo 10.4.
Elispot
The Multiscreen filter plates of 0.45 um (Merck Millipore, MSIPS4W10) were coated sterilely with 2.5 ug mL-1 RBD or MD39 in ELISA coating buffer overnight at 4 ˚C, respectively. Plates were washed three times with PBS and blocked with complete DMEM for 2 h at 37 ˚C while spleens were being prepared. The single-cell suspensions from spleen cells were loaded onto the plates at a suitable density per well and left overnight at 37 ˚C. Antibody-secreting cells (ASC) of spleen cells were detected by All-IN-ONE mouse ELISPOT Accessory kit (Dakewe) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Plates were dried overnight and antigen-specific spots were counted by ImmunoSpot software (Cellular Technology Ltd).
Western blot
The mouse primary B cells from spleens were treated with ferritin or ICOS-RBD nanoparticles for 36 hours, followed by cell lysis and protein immunoblotting. To perform WB, the cells were lysed with RIPA buffer with protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche). Equal amounts of cells lysates were resolved in SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to PVDF membrane (Millipore, IPVH00010). The membrane was blocked with 5% nonfat milk and incubated with appropriate primary and secondary antibodies. Akt (pan) (40D4) Mouse mAb (CST, 2920) (1:2000 for WB), Phospho-Akt (Ser473) (D9E) XP® Rabbit mAb (CST,4060) (1:500 for WB), Phospho-NF-κB p65 (Ser536) (93H1) Rabbit mAb (CST,3033) (1:1000 for WB), NF-κB p65 (D14E12) XP® Rabbit mAb (CST,8242) (1:1000 for WB), PKC-beta Rabbit mAb (Abclonal, A13628)(1:500 for WB), Phospho-PKC (pan) (βII Ser660) Rabbit mAb(CST, 9371) (1:1000 for WB), Cyclin D2 Rabbit pAb (ABclonal, A1773) (1:1000 for WB), Cyclin D3 Rabbit mAb (ABclonal, A3989) (1:1000 for WB), β-Actin Ab Mouse(Proteintech, 66009) (1:2000 for WB), Goat anti-Rabbit Ab(Licor, 926-32211) (1:10000 for WB), Goat anti-Rabbit Ab(Licor, 925-32280) (1:10000 for WB) The signal intensity of WB bands was quantified by Image J.
Statistical analysis
Pilot studies were used for the estimation of the sample size to ensure adequate power. No samples were excluded from the analyses. Data distribution was assumed to be normal but this was not formally tested. Statistical analyses were performed using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test, or One/Two-way ANOVA with GraphPad Prism 9 as indicated in the Figure legends. Statistical differences with a P value of 0.05 or less were considered significant. All assays were performed at least two times. The exact value of n, which represents the number of mice used in the experiments, is indicated in the Figure legends. Details of statistical analyses and biological replicates are described in each figure legend.