Cell lines
African green monkey kidney Vero cells (CCL-81), HEK293T cells (CRL-3216), and human lung cancer A549 cells (CCL-185) were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells (CCL-243) were purchased from ATCC and cultured in RPMI 1640 with 10% FBS. Expi293F cells were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (R79007) and cultured in Union 293 Cell Feed Medium (Union-Biotech) with 10% FBS. All cells were maintained at 37 °C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Viruses
ZIKV strain GZ02 (GenBank No. KX056898.1) was isolated from a Chinese patient returning from Venezuela in 201667. DENV1 strain Hawaii (GenBank No. EU848545.1), DENV2 strain 16681 (GenBank No. U87411.1), DENV3 strain D191267 (GenBank No. OQ948473.1), and DENV4 strain H241 (GenBank No. AY947539.1) have been described20,68,69. All viruses were propagated in Vero cells.
Mouse-adaptive DENV2 was established according to previously described methods70. In brief, 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were s.c. inoculated with 1 × 104 FFU of DENV2. Three days later, the brains were harvested, homogenized and centrifuged, and the supernatants were used to infect Vero cells. Another three days later, viruses in the culture media were concentrated with Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Unit (100 kDa, Merck Millipore) and s.c. injected into 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice. After 3 alternative passages between Vero cells and the pups, the obtained virus was propagated in Vero cells. Genome sequence of mouse-adaptive DENV2 was analyzed by next-generation and Sanger sequencing (GeneBank No. PQ008452). All the virus stocks were titrated by focus-forming assays in Vero cells and stored at −80 °C.
Recombinant proteins
ZIKV EDIII and NS1 proteins were produced in E.coli and Expi293F cells respectively. In brief, the coding sequence of EDIII (residues 298 to 409 of E protein71) was optimized according to E.coli codon usage, synthesized, and cloned into pET28a with a 6 × His-tag sequence fused at the 5’ terminus. EDIII was expressed in E.coli BL21 (DE3) according to previously described methods72, refolded, and purified by Ni-NTA affinity column chromatography. The coding sequence of NS1 was optimized according to mammalian codon usage, synthesized, and cloned into pVAX1 with a tPA signal sequence fused at the 5’ terminus. After transfection with pVAX1-NS1, the culture supernatants of Expi293F cells were harvested, and NS1 was purified by Ni-NTA affinity column chromatography. The proteins were verified by western blot analysis using human anti-EDIII monoclonal antibody (mAb) 8D1073 and human anti-NS1 mAb 749-A422, respectively. Purified EDIII of DENV1 and E proteins of DENV2-4 were purchased from Sino Biological.
circRNA plasmids
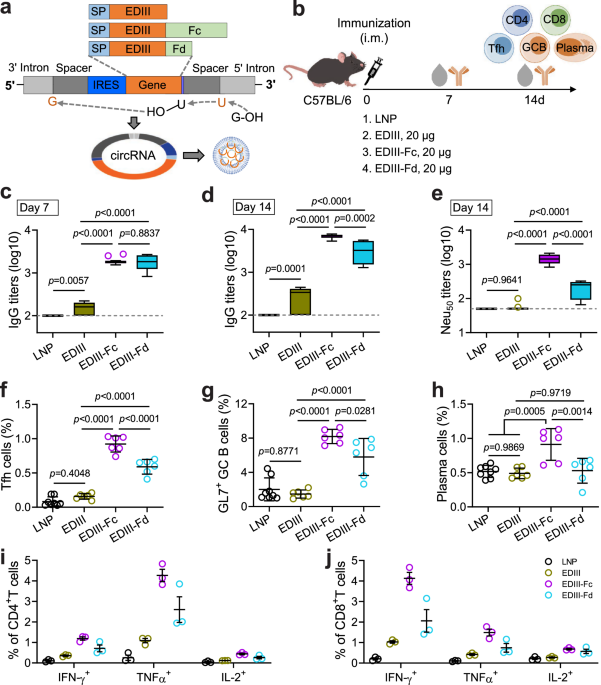
Prototype circRNA vaccines were constructed based on the group I intron sequence of Anabaena pre-tRNA36. In brief, a fragment covering the following elements from 5’ to 3’ terminus was synthesized (Tsingke Biotechnology): 5’ homology arm, 3’ intron, an upstream spacer (5’-GGTAGTGGTGCTACTAACTTCAGCCTGC TGAAGCA-3’), iCVB3, a Kozak sequence (GCCACC), tPA sequence, a downstream spacer (5’-GGTAGTAAACTACTAACTACAACCTGCTGAAGCA-3’), 5’ intron, and 3’ homology arm. The fragment was cloned into pGEM-T-easy backbone (Promega, A1380) (Supplementary Fig. 1a).
Optimized circRNA vaccines were constructed using the group I intron sequence of the Td gene of T4 bacteriophage40. In brief, a fragment covering the following elements from 5’ to 3’ terminus was synthesized (Tsingke Biotechnology): 3’ intron, a 5’ UTR containing an RNA-binding motif of PABPv3 (AAAAAAAAAAAACCAAAAAAAA AAAACAAAAAAAAAAAATAATTGACTAA), iHRV-B3 with an Apt-eIF4G at the proximal loop of domain IV, a Kozak sequence, the tPA sequence, the 3’ UTR of HBA1, and 5’ intron. The fragment was also cloned into pGEM-T-easy backbone (Supplementary Fig. 9a).
The coding sequences of ZIKV EDIII (optimized according to mammalian codon usage), NS1 (optimized according to mammalian codon usage), EGFP, Gluc and Fluc were amplified by PCR and inserted just downstream of the tPA sequence in the pGEM-T-easy vectors mentioned above using ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme). To construct dimeric and trimeric EDIII, the coding sequence of human IgG1 Fc region was fused to the COOH terminus of EDIII to obtain EDIII-Fc, whereas the foldon motif of bacteriophage T4 fibritin protein was fused to the COOH terminus of EDIII with a 4 × GS linker to obtain EDIII-Fd.
Production of circRNAs
All the circRNAs were prepared according to previously described methods36. In brief, DNA templates for circRNA precursors or control linear precursors were amplified by PCR from their respective pGEM-T-easy plasmids. The primers used were as follows. For circRNA precursors, the universal forward, 5’-GCTTTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGG-3’; reverse for Anabaena intron, 5’-CTAGA TATGCTGTTATCCGTCGA-3’; reverse for T4 Td intron, 5’-CTGCAGGTCGACTC TAGAGAA-3’. For control linear precursors, the universal forward primer was the same as mentioned above; reverse for Anabaena intron, 5’-CTCGCCGGTAACGCAT AATAGCC-3’; reverse for T4 Td intron, 5’-GTCAGACTTTATTCAAAGACCACGG G-3’. Compared to circRNA precursors, the corresponding control linear precursors have the 5’ intron truncated and thus cannot be circularized. Program was set up as: 95 °C for 10 min; 30 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 10 s per kilo base pairs (kbp); 72 °C for 7 min. circRNA precursors and control linear precursors were produced using HiScribe T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit (NEB, E2050S). Residual DNA templates were digested with DNase I (NEB, M0303S) at 37 °C for 15-30 min. Total RNAs were extracted using lithium chloride (LiCl, 7.5 M, Thermo Fisher Scientific, AM9480) and quantified using Nanodrop 8000. For circularization, 50 μg circRNA precursors were heated at 70 °C for 5 min and immediately chilled on ice for 5 min. GTP (Thermo Fisher Scientific, R0461) was added at a final concentration of 2 mM along with T4 RNA Ligase Reaction Buffer (containing 10 mM Mg2+, NEB, B0216L) and incubated at 55 °C for 15 min. Finally, circRNAs were extracted by LiCl precipitation, dissolved in nuclease-free water, and subjected to HPLC purification.
RNase R digestion
In brief, 20 μg circRNA or control linear precursors were incubated at 65 °C for 3 min, chilled on ice for 3 min, and added with 20 U RNase R (Epicentre, RNR07250). After digestion at 37 °C for 30 min or 240 min (for NS1 circRNAs only), RNAs were extracted by LiCl precipitation and subjected to agarose-gel electrophoresis.
Junction site PCR
In brief, 10 µg circRNA was treated with RNase R and purified using the MEGAclear Transcription Clean-up kit (Thermo Fisher, AM1908). Control linear precursors were examined in parallel. cDNAs were synthesized using GoScript Reverse Transcription System (Promega, A5001) with random primers. Junction site PCR was carried out using primers as follows. For Anabaena intron junction site, forward, 5’-CAAAACGGCTATTATGCGTTACC-3’; reverse, 5’-ATACCAGAGTG CTAGCGCC-3’. For T4 Td intron, forward, 5’-TAAGCTGGAGCCTCGGTG-3’; reverse, 5’-GTTCAGGAAGGGTACAATGGG-3’. Program was set up as: 95 °C for 10 min; 25 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 10 s; 72 °C for 1 min. PCR products were subjected to agarose-gel electrophoresis and Sanger sequencing.
HPLC purification
In brief, after LiCl precipitation, circRNA mixtures were loaded onto a 10 × 300 mm size exclusion column with particle size of 5 μm and pore size of 2000 Å (Sepax Technologies, 215980P-10030) and eluted with RNase-free TE buffer (pH = 8.0, Coolaber, SL2082) on an Agilent 1260 Series HPLC (Agilent) at a flow rate of 1.65 ml/min. Fractions were collected as indicated, quantified by measuring the absorption values at 260 nm, and subjected to agarose-gel electrophoresis. circRNAs were then enriched using Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter (50 kDa, Merck Millipore) and dissolved in RNase-free water.
LNP encapsulation
circRNAs were encapsulated with LNPs according to previously described methods74. In brief, circRNA-LNPs were formulated by mixing the ethanol phase containing ionizable lipids (SINOPEG, SM102/DSPC/cholesterol/DMG-PEG 2000 at molar ratios of 50:10:38.5:1.5) with the aqueous phase containing circRNA in acetate buffer (pH = 5.0) at a ratio of 3:1 (lipids: RNA) on a microfluidic chip device (Micro & nano). circRNA-LNPs were then re-suspended in PBS (pH = 7.4) and filtered using Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter (10 kDa, Merck Millipore). Encapsulation rates and circRNA concentrations were measured using the Quant-it RiboGreen RNA Assay Kit (Invitrogen, R11490). The size of circRNA-LNPs was measured using dynamic light scattering (Malvern Zetasizer) and analyzed using Zetasizer software.
circRNA transfection assay
In brief, HEK293T or A549 cells were transfected with each circRNA (for 24-well plates: 2, 1, 0.5 or 0.2 μg per well; for 96-well plates: 200, 100, or 50 ng per well) using Lipofectamine MessengerMax (Invitrogen, LMRNA003), following the manufacturer’s instructions. To test the expression of EDIII or NS1, cell lysates and culture media were harvested at 24 or 48 h after transfection and subjected to western blot analysis. To test the expression of EGFP, A549 cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus) and images were captured at 48 h after transfection. The Fluc in cell lysates and Gluc in culture media were tested at 24 h after transfection using Luciferase Assay System (Promega) or coelenterazine (Coolaber), respectively. RLUs were recorded by GloMax Discover Microplate Reader (Promega).
Western blot analysis
In brief, cell lysates or culture media were added with loading buffer in the presence or absence of β-mercaptoethanol. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare). After blocked with 5 % skimmed milk in PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 (PBST) at 37 °C for 1 h, membranes were incubated with anti-ZIKV E mAb 8D10, anti-ZIKV NS1 mAb 749-A4, EDIII protein immune mice sera, or mouse anti-GAPDH antibody (Beyotime) at 4 °C overnight. After thoroughly washed with PBST, membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-human or anti-mouse IgG antibodies for 1 h (Beyotime) and developed with chemiluminescent substrates (GeneStar). Protein signals were captured by chemiluminescent Western blot imaging system (Biorad).
Animals
Eight-week-old C57BL/6 mice and CD-1(ICR) mice were purchased from GemPharmatech Co., Ltd. Ifnar−/− C57BL/6 mice were constructed by CRISPR-Cas9 technology at Cyagen Biosciences. All animals were bred and housed in the Animal Experimental Center of Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health (GIBH). Mice were housed in an SPF barrier facility with 12 h/12 h light/dark cycles, a temperature of 20–23 °C, and humidity of 50-60%. Challenge assays involving ZIKV or DENV were conducted under animal biosafety level 2 (ABSL-2) plus conditions. All experiment protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of GIBH (IACUC, No. 2021061).
Immunization and challenge assays
To test the immunogenicity of EDIII, EDIII-Fc or EDIII-Fd circRNA (Figs. 1, 2), 8-week-old C57BL/6 mice (female), or 12-week-old Ifnar−/− C57BL/6 mice (male and female) were i.m. immunized once or twice (at a 3-week-interval) with circRNA-LNP (containing 20 μg circRNA per mouse) in 200 μl PBS. Control mice received an equal mass of empty LNPs or equal volume of PBS. Sera, spleens, or inguinal lymph nodes were harvested at the indicated time points and subjected to antibody or lymphocyte examination.
To test the immunogenicity of prototype and optimized EN(LNP) (Figs. 3, 4, 6), 8-week-old C57BL/6 mice (female) or 12-week-old Ifnar−/− C57BL/6 mice (male and female) were i.m. immunized once or twice (at a 3-week interval) with EN(LNP), EN(RNA), EDIII-Fc circRNA, NS1 circRNA, optimized EN(LNP), or the m1Ψ-modified mRNAs at 5 or 20 μg each RNA as indicated. Sera or inguinal lymph nodes were collected and subjected to antibody or lymphocyte examination.
To test the protective effects of circRNA vaccines, two models were used. For the maternal immunization and neonatal challenge model, immunized female C57BL/6 mice were mated with unimmunized male mice at 2 (Figs. 2–4), 3 (Fig. 6), or 8 (Fig. 7) weeks after the final immunization. After birth, 1-day-old pups were s.c. injected with 1 × 104 FFU of ZIKV in 50 μl PBS. HC pups received 50 μl PBS via the same route. Body masses and symptoms were recorded daily. Pups that showed continuous loss of body mass for two days were considered dead and euthanized. At 15 days after challenge, neurological scores, mainly the paralysis of limbs and tail, were recorded in a single-blind manner. Pups were sacrificed and brain tissues were harvested and subjected to viral load detection or histological analysis.
For the adult Ifnar−/− C57BL/6 mice model, immunized mice (male and female) were s.c. challenged with 1 × 105 FFU of ZIKV in 100 μl PBS at 12 days (Supplementary Fig. 6) or 3 weeks (Figs. 2 and 6) after the final immunization. HC mice received 100 μl PBS via the same route. Body masses were recorded daily. Mice that had lost 20% of initial body mass were considered dead and euthanized. Sera were collected at 1, 4, and 7 days after challenge. At 10 or 15 days after challenge, mice were sacrificed. Sera, brains, and spleens were harvested and subjected to viral load detection.
To test the virulence of mouse-adapted DENV2 in mice, 1-day-old CD-1(ICR) mice were intracerebrally challenged with 1 × 104 FFU of parental or mouse-adapted DENV2. Body masses and symptoms were recorded daily.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
In brief, 96-well ELISA plates were coated with purified ZIKV EDIII, DENV1 EDIII, E proteins of DENV2-4, or ZIKV NS1 at 50 ng per well at 4 °C overnight. After washed 3 times with PBST, plates were blocked with PBST containing 5% skimmed milk at 37 °C for 1 h. Mice sera were 4-fold serially diluted (starting from 1:100 or as indicated), added to each well, and incubated at 37 °C for 2 h. LNP- or PBS-immunized mice sera were used as negative controls. After washed 3 times with PBST, plates were added with an HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody (Beyotime), incubated at 37 °C for 1 h, and washed 5 times with PBST. The reactions were developed with 100 μl TMB/E substrates (Merck Milipore) and terminated with 2 M H2SO4. Finally, OD450 values were recorded by Microplate Reader Epoch2 (BioTek). IgG titers were calculated as the reciprocals of the maximal dilutions at which the OD450 values were equal to or higher than the cut-off values (2.1 times that of the negative control wells).
Flow cytometry-based neutralization test (FNT)
FNT was performed according to previously reported methods39. In brief, Vero cells were seeded into 96-well plates at 2 × 104 cells per well and cultured overnight. Mice sera were 4-fold serially diluted in DMEM (starting from 1:50 or 1:100) and incubated with ZIKV (200 FFU per well) at 37 °C for 1 h. LNP- or PBS-immunized mice sera were used as negative controls. The mixtures were added onto cells, incubated at 37 °C for 2 h, and replaced with fresh DMEM containing 2% FBS. Three days later, cells were fixed and permeabilized with Cytofix/Cytoperm buffer (BD). Cells were then labeled with mAb 8D10, stained with an Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated goat anti-human IgG antibody (SouthernBiotech, 2040-31), and analyzed on Accuri C6 flow cytometer (BD). Half-maximal neutralizing antibody (Neu50) titers were calculated as the dilutions at which the E-positive cells were reduced by 50% relative to negative controls.
Flow cytometry of Tfh, GC B and plasma cells
In brief, lymphocytes were isolated from the ILNs by passing through 200-mesh stainless steel wire meshes. Cells were blocked with an Fc receptor antibody α-CD16/32 (clone: 2.4G2) on ice for 5 min, followed by staining with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies in PBS with 2% FBS: for the Tfh cell panel, CD3 (PerCP/Cy5.5, clone: 17A2, BioLegend), CD4 (APC, clone: RM4-5, BD), CXCR5 (PE, clone: 2G8, BD), PD-1 (BV421, clone: EH12.1, BD); for the GC B cell and plasma cell panels, CD45R (PE/Cy7, clone: RA3-6B2, BD), CD38 (PerCP/Cy5.5, clone: 90/CD38, BD), CD138 (PE, clone: 281-2; BD), CD95 (BV421, clone: Jo2, BD), GL7 (Alexa Fluor 647, clone: GL7, BD). The staining was performed on ice for 30 min. Finally, cells were fixed and analyzed by LSRFortessa (BD).
Intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) assay
In brief, lymphocytes were isolated from the spleens by passing through 200-mesh stainless steel wire meshes followed by density gradient centrifugation using mouse lymphoid separation medium (Dakewe). Cells were seeded into 96-well plates (2 × 106 cells per well) and stimulated with overlapping peptide pools (2 μg/ml of each peptide) corresponding to ZIKV E protein. Unstimulated cells were used as controls. After incubated at 37 °C for 2 h, cell cultures were added with brefeldin A (10 mg/ml; BD) and incubated at 37 °C for another 10 h. After washed twice with PBS, cells were blocked with mAb α-CD16/32 on ice for 5 min and stained with the following surface marker antibodies in PBS (containing 2% FBS) on ice for 30 min: CD3 (BV421, clone: 17A2, BioLegend), CD4 (APC, clone: RM4-5, BD), and CD8α (FITC, clone: 53-6.7, BioLegend). Cells were then fixed and permeabilized with Cytofix/Cytoperm buffer at 4 °C for 30 min. Finally, cells were stained with intracellular antibodies against IFNγ (PE, clone: XMG1.2, BD), TNFα (APC/Cy7, clone: MP6-XT22, BioLegend) and IL-2 (BV605, clone: JES6-5H4, BioLegend) and analyzed on LSRFortessa.
Neurological scoring
On day 15 after challenge, neurological symptoms of the pups were scored in a single-blind manner39. Scores of each limb were designated as: 0, no sign; 1, weakness or altered gait; 2, paresis; 3, full paralysis. Scores of the tail were designated as: 0, no sign; 1, half paralysis; 2, full paralysis. The score of one pup was the sum of the scores from four limbs and the tail. Accordingly, the maximal score of a survival pup is 14. A pup that succumbed to infection received a score of 15.
Histological analysis
In brief, brain tissues were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 7 days and transferred to 70% ethanol. Subsequently, brain tissues were dehydrated via a serial ethanol gradient and embedded in paraffin wax blocks. Tissue sections (5-mm-thick) were prepared, dewaxed in xylene, rehydrated via decreasing concentrations of ethanol, and washed with PBS. Tissue sections were then stained with hematoxylin for 8 min and eosin for 3 min. Finally, tissue sections were successively incubated with 70% ethanol for 20 s, 90% ethanol for 20 s, 100% ethanol for 1 min, and xylene for 3 min. Images were captured using TissueFAXS (TissueGnostics). The meningeal inflammation and cortex laminar necrosis were assessed in a single-blind manner. In brief, five versions in cerebral cortex were randomly selected for each section and scored. Scores of meningeal inflammation were designated as: 0, no lymphocyte infiltration; 1, mild lymphocyte infiltration; 2, moderate lymphocyte infiltration; 3, severe lymphocyte infiltration. Scores of cortex laminar necrosis were designated as: 0, no signs of necrosis; 1, mild necrosis; 2, moderate to severe necrosis. Accordingly, the maximal pathological score of one version is 5. The median score of the 5 versions were designated as the score of that mice.
Quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Genome copy numbers of ZIKV or DENV2 in the sera or tissues were measured using qRT-PCR as described previously39,75. In brief, total RNAs were extracted using TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific). qRT-PCR was carried out using HiScript II One Step qRT-PCR SYBR Green Kit (Vazyme). The primers used were as follows. For ZIKV, forward, 5’-TGGAGGCTGAGGAAGTTCTA G-3’; reverse, 5’-CTTCACAACGCAATCATCTCCACTG-3’. For DENV2, forward, 5’-CAGGTTATGGCACTGTCACGAT-3’; reverse, 5’-CCATCTGCAGCAACACCAT CTC-3’. Program was set up as: 50 °C for 30 min; 95 °C for 10 min; 45 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. Melting curves were produced at 65 °C to 95 °C with an increment of 0.5 °C per cycle for 5 s. Standard curves were created using ZIKV RNAs corresponding to NS5 or DENV2 RNAs corresponding to E, which were generated by IVT. Viral loads were calculated as genome copy numbers per gram tissues or per ml sera. LODs were about 1 × 104 copies per gram tissues or 1 × 102 copies per ml sera.
In vitro ADE assay
ADE effects of immune sera in cell cultures were measured using a flow cytometry-based assay20. In brief, mice sera were 5-fold serially diluted (starting from 1:100), mixed with ZIKV or DENV3 (1 FFU per cell), or with DENV1, DENV2, or DENV4 (0.2 FFU per cell) in RPMI 1640, and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. C57BL/6 mice sera collected 2 weeks after ZIKV infection (1 × 105 FFU, s.c.) were also tested. The mixtures were added to K562 cells in 96-well plates and incubated at 37 °C for 2 days. Cells were fixed and permeabilized using Cytofix/Cytoperm buffer, and labeled with anti-ZIKV mAb 8D10, or with mAb ZK8-4 which was isolated from a ZIKV-infected patient and showed cross-reactivity to DENV E proteins76. Finally, cells were stained with an Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated goat anti-human lgG antibody (SouthernBiotech, 2040-31) and analyzed using Accuri C6 flow cytometer.
In vivo ADE assay
For the passive transfer model, the immune sera collected at 2 or 8 weeks after the final immunization were equally pooled for each group, inactivated by incubation at 56 °C for 30 min, and diluted tenfold with PBS. Twelve-week-old Ifnar−/− C57BL/6 mice (male and female) were i.p. administrated with 200 μl diluted sera (equal to 20 μl pooled sera). One day later, mice were i.p. challenged with 1 × 106 FFU of mouse-adapted DENV2. The body masses and survival rates were monitored daily. Sera were collected at 1, 4, and 7 days after challenge and DENV2 genomes were measured by qRT-PCR. Mice that lost 20% of initial body mass were considered dead and euthanized.
For the active immunization model, 12-week-old Ifnar−/− C57BL/6 mice (male and female) were i.m. immunized with prototype or optimized EN(LNP) at 20 μg each circRNA per mouse, or 1 × 105 FFU of ZIKV which had been inactivated with 0.2% β-propiolactone and added with aluminum adjuvant, or an equivalent mass of empty LNPs. Mice receiving 200 μl diluted ZIKV sera 1 day before challenge were also used as controls. At 2 (Fig. 5f) or 3 (Fig. 8g–i) weeks after immunization, mice were challenged with 1 × 106 FFU of mouse-adapted DENV2. The survival, body masses, and serum viral loads were monitored or tested similarly.
Data process and statistics
Flow cytometry data were analyzed using FlowJo software v10 (BD). Comparisons between two groups were conducted by paired or unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. Comparisons among more than two groups were conducted by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison tests. Comparisons of the survival data were conducted by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) tests. Statistical analyses were computed by GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad) and the details have been provided in each figure’s legend. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data graphs were constructed using GraphPad Prism 8. Figures were created using Adobe Illustrator 2021 (Adobe Systems Inc.) and PowerPoint 2013 (Microsoft).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.