Study design and participants
UK Biobank
Study participants were from the UK Biobank study, a population-based cohort of more than 500,000 participants from England (89%), Wales (7%) and Scotland (4%). From 2006 to 2010, all people registered on the National Health Service register, aged 40–69 years and living less than 40 miles from the study center, were invited to participate. 503,325 participants were recruited from 9.2 million mailed invitations. The study design and participant characteristics have been previously described in detail elsewhere 29.
The UK Biobank includes information on demographics, socio-economic and lifestyle factors, physical indicators and medical history. This also includes genotyping data 30 and follow-up data via links to electronic medical record databases.
COVID-19 Self-Testing Antibody Seroprevalence Study
Surviving UKB participants were invited to participate in a SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus antibody seroprevalence survey from February 2021 to July 2021. At the same time, the UK’s vaccination program was being implemented. All participants who met the inclusion criteria, regardless of gender, age, or health status, were eligible for recruitment and, as a result, received an email with an invitation and brief information about the study. Participants who were unable or unwilling to participate were encouraged to inform them of their decision. Seven days after the initial invitation, a remaining email was sent to participants who had not yet responded. Those wishing to participate were asked to confirm their contact details and agree to receive a lateral flow self-test kit at their home address. Participants’ addresses were securely forwarded to a third-party postal and shipping company, and participants were sent an email 3 days prior to kit shipment notifying them that their kit would be shipped.
Once participants had completed their test, they were asked to complete an online UK Biobank survey. The questionnaire collected information on results (IgM or IgG positive, negative, or invalid), test date, first and second COVID-19 vaccination status, and date. The date on which participants submitted their results will be automatically recorded. A reminder email was sent to participants who did not return their test results one week after the kit was shipped.
Recruitment occurred in two stages. In the first phase, approximately 34,713, 22,390, and 21,405 participants were invited, respectively. In the second stage, we invited the remaining approximately 371,985 participants who were not eligible in the first stage. For further details on the study design, please see the online document https://biobank.ndph.ox.ac.uk/showcase/label.cgi?id=998.
Seroprevalence study of novel coronavirus infection
The lateral flow test device used in the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus antibody seroprevalence study was unable to distinguish between antibodies induced by infection or vaccination. Therefore, people who have previously participated in an autoantibody testing study, those who have reported a positive test result, and those who have reported having been vaccinated before taking an antibody test will be eligible to receive a capillary blood sample for the antibody test. were invited again to provide samples. IgG antibody against nucleocapsid (N) protein. This indicates a past COVID-19 infection. Recruitment of participants for the COVID-19 study is similar to recruitment for the antibody study and details are provided in the online document: https://biobank.ndph.ox.ac.uk/showcase/label.cgi ?id=997.
Data linkage
Follow-up of UK Biobank participants will occur through individual-level linkages with multiple electronic health databases. The databases used in this study include primary care records (prescriptions and diagnoses), inpatient admissions (diagnoses), death registries, and national infectious disease surveillance data (COVID-19 test results). Mas31.
Genotyping and imputation
Genotyping and quality control of the UK Biobank genetic dataset has been previously described 30. In summary, the UK Biobank genotype calling was performed by Affymetrix and includes 784,256 autosomal variants. Imputation was performed by combining two different reference panels: the Haplotype Reference Consortium (HRC) and the UK10K Haplotype Resource. This includes 93,095,623 autosomal SNPs.
Definition of study cohort
In this study, we analyzed four different cohorts to study genetic variation associated with four different traits: (1) induced by a single dose of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccine; seroconversion, (2) seroconversion induced by two doses of COVID-19 vaccine, (3) ) susceptibility to breakthrough infection, and (4) severity of breakthrough infection.
In the main analysis, individuals who do not have European genetic ancestry, have sex chromosome aneuploidy, and whose genetic sex differs from their registered sex are not included in the main analysis to avoid confounding effects. It was.
Seroconversion responders and non-responders
For the seroconversion groups (one-dose, two-dose), we first restricted the analysis to vaccinated UK Biobank participants enrolled in the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence study.
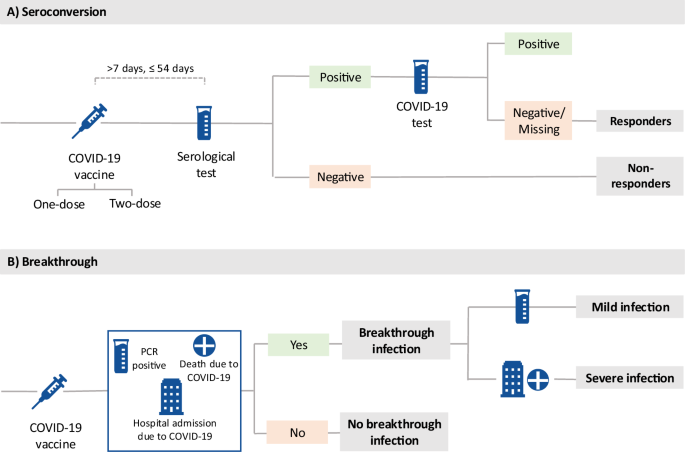
Responders were defined as participants who had a positive serology test (from the COVID-19 Self-Test Antibody Seroprevalence Study) within 8 to 56 days after vaccination. However, individuals who had evidence of previous COVID-19 infection after a seropositive result (positive result from a COVID-19 seroprevalence study) were excluded from the cohort. Non-responders were participants who had negative serology within 8 to 56 days after vaccination (see Figure 1A).
Breakthrough susceptibility and severity
For the breakthrough group (breakthrough susceptibility, breakthrough severity), we included UK Biobank participants who had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccination.
A breakthrough susceptibility infection is defined as a positive PCR test, hospitalization diagnosed with COVID-19 (ICD-10 codes: U07.1, U07.2), or a death certificate listing COVID-19 as the cause of death (same ICD ) defined by -10 codes). Participants with no breakthrough infection are participants who did not have a positive PCR test, were not hospitalized with a diagnosis of COVID-19, and did not have COVID-19 listed as the cause of death on their death certificate. It was. Among breakthrough infectious disease cases, we defined severe cases of novel coronavirus infection that require hospitalization or lead to death. The mildly infected individuals included in the innovative severity analysis were participants who received only a PCR test (see Figure 1B). For more information on ICD-10 codes, see Supplementary Note 1.
Genome-wide association research
We conducted four different genome-wide association studies: one-dose seroconversion, two-dose seroconversion, breakthrough susceptibility, and breakthrough infection. Associations between variants and traits were calculated using the machine learning method REGENIE (version 1.0.5)32. Briefly, REGENIE fits genome-wide regression models in two major steps. In step 1, a genome-wide regression model is fitted using a subset of the total set of available genetic markers. In step 2, a larger set of markers is tested for association with the trait of interest, conditional on the predictions from the regression model in step 1.
In our study, we used UK Biobank genotype calls in the first step and UK Biobank imputation data in the second step. Regression models were adjusted for baseline age (antibody test date), gender, genetic batch, and the first 10 genetic principal components. We also applied first-order corrections in case of imbalance. Variants (genotype calls and imputation data) in both datasets underwent quality control before being used for analysis. Quality control was performed using PLINK2 (version 1.0.6)33. Excluded variants include variants with missing genotype data, variants that deviate from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (P < 1 × 10−15), and variants with minor allele frequency <1%. For imputed variants, we also removed duplicate SNPs and kept only the first instance.
After performing a genome-wide association study, variants with p-value ≤ 5 × 10−8 were considered to have a statistically significant association with the trait. The effect size of the genetic association for each SNP was measured using the odds ratio (OR). We used FUMA (version 1.6.0)34 to identify read-independent significant SNPs (r ≤ 0.1) and top read-independent significant SNPs from each locus (window 250 kb). I did. SNPs were mapped to genes using positional mapping (window 10 kb).
Data curation to generate analysis cohorts and results was performed using R software (version 4.3.0). GWAS was performed on the UK Biobank RAP platform. Plots were generated in R.
verification
To study whether the associations obtained in European populations are replicated in other ancestral groups, we tested the associations of independent variants using non-European populations. This analysis used the complete genotype calling data in the first step of the REGENIE method. Subsequently, in the second step, only the lead-independent significant SNPs obtained in the main analysis were tested.
The OR from the main analysis and the validated OR point in the same direction (OR and ORv, both >1 or <1)、検証された p 値 (Pv) ≤ 0.05 を持つバリアントが完全に検証されました。両方の OR が同じ方向であるが、検証された p 値 > Variants with 0.05 were partially validated. Variants containing reverse ORs were not validated.
colocalization
Once we have the mutations associated with one-dose vaccine seroconversion, two-dose vaccine seroconversion, breakthrough infection, and breakthrough severity, we aim to study the genetic overlap between different traits. I did. First, we studied the association of all lead-independent mutations across all traits. We then performed colocalization analysis within ±250 kb of each locus using the R package coloc35. Colocalization analysis can assess whether the same trait has similar genetic roots. We adopt the default prior probabilities of colocalization, P1 = 10−4, P2 = 10−4, and P12 = 10−5, and effectively reduce the posterior probability of greater than 50% for the common causal variant assumption (H4). considered as evidence. Colocalization.
Software/Implementation
To perform the GWAS, we used the UK Biobank RAP platform, specifically the software REGENIE32 (version 1.0.5) and PLINK233 (version 1.0.6). FUMA34 (version 1.6.0) was used to detect independent SNPs. Data manipulation was performed in R software (version 4.3.0), and the main packages used were coloc36 (version 5.2.3), dplyr37 (version 1.1.3), and ggplot2 (version 3.5.1).
Report overview
For more information on the study design, please see the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked in this article.